What is a Blower Pump and How Does It Work?
Blower pumps play a vital role in various industries. They ensure efficient gas and liquid transfer processes. A recent industry report noted that the market for blower pumps is projected to grow significantly, achieving a CAGR of 6.5% by 2027.
These pumps operate differently from traditional pumps. They move air or gas through positive displacement mechanisms. This unique operation makes them ideal for handling low-viscosity fluids. Many facilities rely on blower pumps for pneumatic conveying systems. However, maintenance can sometimes be overlooked, leading to efficiency issues.
Understanding how a blower pump functions is essential for operations. Implementing regular check-ups and ensuring proper installation can enhance performance. Despite their advantages, some challenges persist, such as noise levels and energy consumption. Addressing these concerns is crucial for long-term effectiveness.
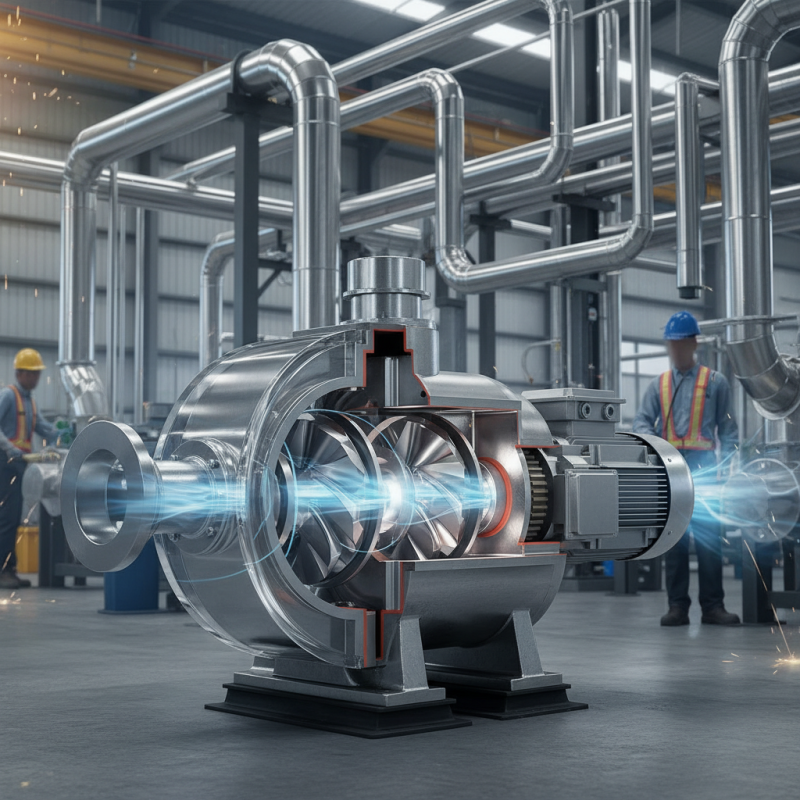

What Is a Blower Pump: An Overview of Its Functionality
Blower pumps play a critical role in various industries, including wastewater treatment and food production. These devices move air or gas through a system to achieve desired pressure levels. A blower pump increases airflow effectively, ensuring processes run smoothly. According to recent industry reports, the global blower market is expected to reach $12 billion by 2025, demonstrating its growing importance.
The functionality of a blower pump is quite straightforward. It relies on positive displacement or centrifugal principles to function. The positive displacement design traps air in a specific volume, then forces it out under pressure. In contrast, centrifugal fans rapidly spin, moving air through an impeller. However, the choice between these types can be perplexing. Factors like efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance requirements complicate decision-making.
Operators must consider the operating environment and specific application. High humidity levels or the presence of corrosive substances dramatically affect performance. A report from the International Energy Agency highlights that improper selection can lead to energy inefficiencies of up to 30%. Therefore, assessing applications and conditions is essential for optimal performance. Missteps can incur significant long-term costs, making thorough analysis crucial.
Principles of Operation: How Blower Pumps Generate Airflow
Blower pumps are vital in various industries. Their primary role is generating airflow through mechanical processes. Understanding their operational principles is crucial for their effective use. These pumps typically use rotary mechanisms. These mechanisms create a vacuum, which pulls in air and compresses it.
During operation, air enters the pump chamber via an inlet. Once inside, the rotor spins. This motion traps air in pockets, reducing its volume. As a result, pressure increases. The compressed air is then released through the outlet. This simple yet efficient design allows for consistent airflow. Reports indicate that blower pumps can achieve an efficiency of over 75% in optimal conditions.
However, challenges exist. Maintaining proper lubrication is vital. Low lubrication can lead to overheating, impacting performance. Monitoring pressure fluctuations is equally essential. Neglecting these aspects may cause unexpected downtime. Data suggests that effective maintenance can extend pump life by up to 30%. Regular assessments help in identifying potential issues early, which is crucial for reliable operation.
Blower Pump Performance Analysis
This chart illustrates the airflow generated by different types of blower pumps at varying RPMs (Revolutions Per Minute). The data shows how airflow increases with RPM, helping users understand the operational efficiency of blower pumps.
Key Applications of Blower Pumps in Various Industries
Blower pumps play a crucial role in various industries. They move air or gas efficiently in systems. One key application is in wastewater treatment. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, about 70% of treatment plants in the U.S. use blower pumps for aeration. This ensures that microorganisms break down waste effectively.
In the food and beverage industry, blower pumps are vital for maintaining quality. They help in transporting ingredients, ensuring that processes run smoothly. Studies show that over 60% of food processing plants rely on this technology for efficiency and hygiene standards. Efficient operation leads to lower energy costs, which is a priority for many businesses today.
**Tips:** Choose the right size blower pump for your application. An oversized pump can waste energy. Regular maintenance is essential. Neglecting it can lead to costly breakdowns. Be aware of the noise levels; they can impact workplace comfort. A poorly placed pump may create unwanted disturbances.
What is a Blower Pump and How Does It Work? - Key Applications of Blower Pumps in Various Industries
| Application Industry | Blower Pump Function | Typical Capacity Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Treatment | Aeration for biological filtration | 10 to 2000 CFM | Energy-efficient, continuous operation |
| Food and Beverage | Conveying ingredients and products | 5 to 500 CFM | Hygienic design, low pulsation |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drying and packaging processes | 1 to 100 CFM | Sterile operation, precise control |
| Aquaculture | Oxygenation of water bodies | 50 to 1000 CFM | Durability, high efficiency |
| Chemical Processing | Transfer of gases and vapors | 10 to 1500 CFM | Corrosion-resistant materials |
Comparative Analysis: Blower Pumps vs. Traditional Pump Systems
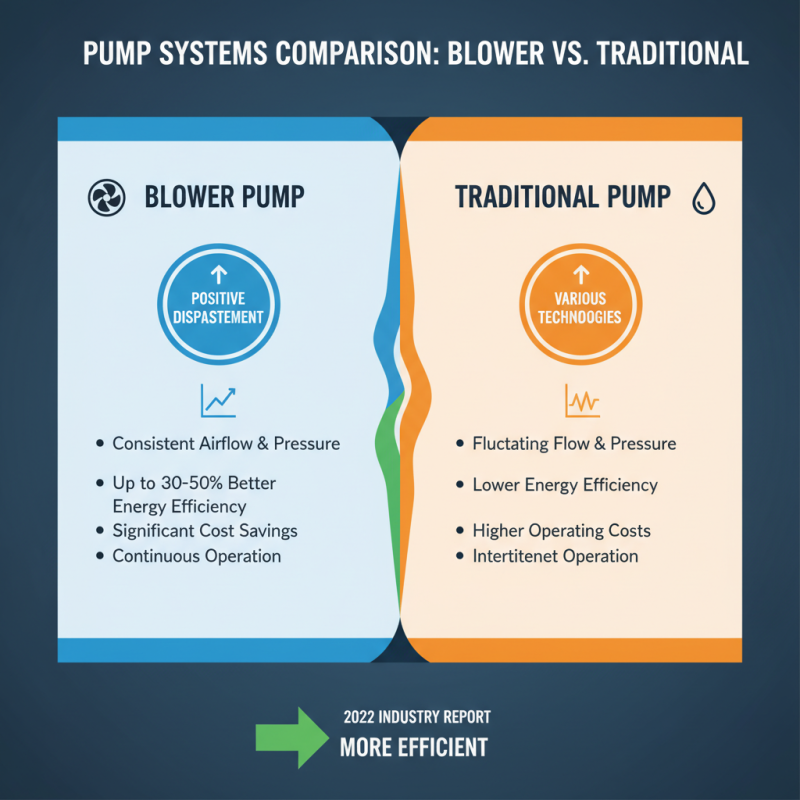
Blower pumps and traditional pump systems serve similar purposes but differ significantly in operation and efficiency. Blower pumps utilize positive displacement technology. This allows for consistent airflow and pressure. According to a 2022 industry report, blower pumps can achieve up to 30-50% better energy efficiency compared to conventional systems. This efficiency can lead to significant cost savings in operations.
In contrast, traditional pumps often rely on dynamic methods, which may lead to pressure fluctuations. These fluctuations can stress components and reduce the lifespan of the system. A study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers found that nearly 60% of traditional pump users experience performance issues due to these inconsistencies. Moreover, maintenance concerns arise more frequently with traditional systems. Users often report higher downtime costs associated with repairs.
While blower pumps have their advantages, they are not without drawbacks. Some applications may require more complex installations. This complexity can lead to higher initial setup costs. Additionally, not all processes benefit equally from the advantages of blower pumps. In some scenarios, traditional pumps might still be the preferred option based on specific operational needs.
Maintenance and Efficiency: Maximizing Blower Pump Performance
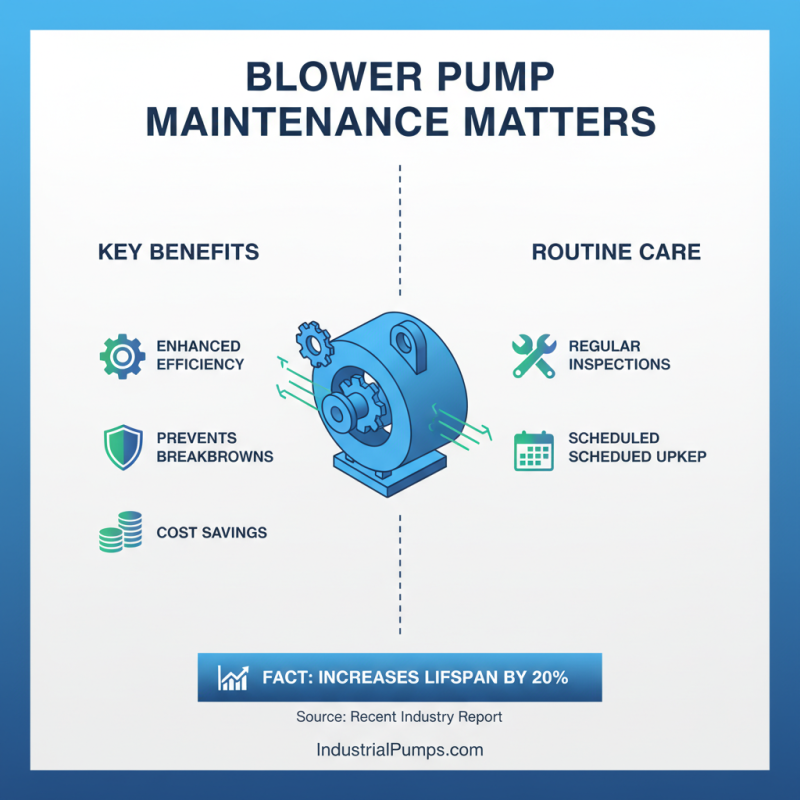
Blower pumps are crucial in many industries. Regular maintenance enhances their efficiency. Keeping these pumps in top shape prevents breakdowns and costly repairs. According to a recent report, routine inspections can increase pump lifespan by 20%. This means companies save significantly on operational costs.
Efficient blower pumps contribute to energy savings. The U.S. Department of Energy states that optimizing pump systems can cut energy use by 10% to 30%. Simple practices, like checking for leaks and ensuring proper alignment, can make a difference. Many facilities overlook these steps, leading to reduced performance.
Ignoring minor issues can escalate into major repairs. For instance, a clogged filter can decrease airflow. This situation causes extra strain on the pump, leading to inefficiency. Employing a scheduled maintenance plan can help catch these problems early. Investing time in pump upkeep proves beneficial in the long run.
Related Posts
-
Why Choose a Blower Pump for Your Next Project and How It Benefits You
-
Top 10 Blower Pumps for Efficient Air Movement and Optimal Performance
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Vacuum Blower Pump for Your Needs
-

10 Custom Engineering Tips to Boost Your Project Efficiency by 40% in 2023
-
How to Choose the Right Suction Pump for Your Specific Needs
-

Innovative Dry Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps Showcase Growth Prospects at the 2025 China 138th Export Commodities Fair